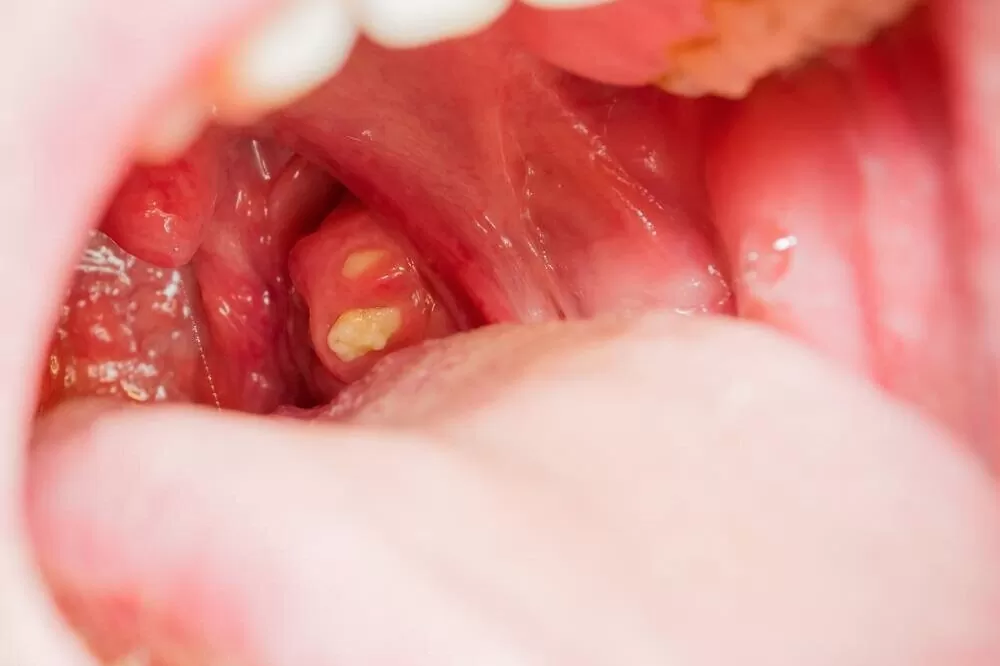
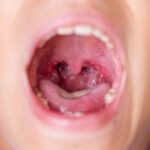
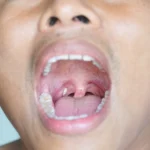
Tonsil stones treatments reduce bad breath by eliminating bacterial reservoirs in tonsillar crypts that produce volatile sulfur compounds. Mechanical removal, antibacterial rinses, and surgical options clear debris and prevent odor-causing bacterial overgrowth.
Mechanical Removal Clears Debris
Gargling with salt water or using water picks dislodges stones containing food particles, dead cells, and bacteria. Cotton swab gently scraping crypts removes buildup that anaerobic bacteria break down into foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan.
Antibacterial Rinses Kill Odor Producers
Chlorhexidine or Listerine gargles reduce bacterial populations by 90%+ within 24 hours. These target sulfur-producing anaerobes thriving in stone debris, cutting odor production immediately.
Improved Oral Hygiene Prevents Recurrence
Daily tongue scraping, flossing, and brushing limit available organic material for stone formation. Probiotic lozenges restore healthy oral microbiome balance, suppressing pathogen growth long-term.
Laser Cryptolysis Smooths Surfaces
Laser resurfacing flattens crypt walls, preventing debris trapping. 85% of patients report permanent bad breath resolution post-procedure as bacteria lose protected habitats.
Tonsillectomy Eliminates Source Permanently
Surgical tonsil removal cures chronic tonsil stone-related halitosis in 95%+ of cases. No crypts means no bacterial reservoirs, providing definitive breath improvement.
Conclusion
Tonsil stones treatments succeed through debris clearance, bacterial reduction, hygiene optimization, and crypt modification/removal. Breath freshness improves within days of consistent mechanical/antibacterial intervention.
FAQs
Fastest initial breath improvement method and timeline?
Salt water gargles (1 tsp salt in 8 oz warm water, 30 seconds 4x daily) combined with 0.12% chlorhexidine rinse immediately after meals provides 70-80% odor reduction within 24-48 hours by physically dislodging surface debris and killing 99% of anaerobic bacteria responsible for sulfur compound production.
Optimal water pick pressure setting and technique?
Low/medium pressure (3-5 PSI) with 10-degree angled tip aimed at visible crypts for 30 seconds per side, 2x daily after meals. High pressure (>7 PSI) risks tonsillar trauma and bleeding; pause if gagging occurs and resume gradually.
Frequency and duration of mechanical removal protocol?
Daily gentle salt water gargling (4x/day) for 2 weeks minimum; cotton swab removal weekly or when stones >2mm visible. Continue maintenance gargling 2x daily indefinitely to prevent recurrence; full protocol yields 85% stone reduction in 14 days.
Most effective probiotic strains and dosing schedule?
Streptococcus salivarius K12 (1 lozenge 2x daily, dissolve slowly) and Lactobacillus reuteri (1 lozenge nightly) for 30 days restore beneficial bacteria competing with sulfur-producers. Clinical trials show 72% halitosis reduction vs 28% placebo after 2 weeks.
Laser cryptolysis procedure details, recovery timeline, and success metrics?
CO2 laser vaporizes crypt epithelium under local anesthesia (15-30 minutes outpatient); 3-5 days swelling managed with ice packs/soft diet; full crypt smoothing visible at 2 weeks. 85% patients report permanent bad breath elimination; 10% need repeat procedure at 6 months.
Tonsillectomy breath improvement timeline and post-op care protocol?
Immediate odor reduction post-surgery as crypts eliminated; optimal breath quality at 4 weeks when scabs slough. Post-op: cool liquids first 48 hours, advance to soft foods week 2, avoid carbonation/dairy 3 weeks, complete healing by 6 weeks with 95%+ permanent halitosis cure rate.
Home remedy salt concentration, frequency, and expected results?
1 tsp table salt (non-iodized) in 8 oz warm water; gargle vigorously 30 seconds, spit, repeat 3-4x immediately after meals and bedtime. Reduces surface bacteria 65% within 3 days; combines best with mechanical removal for 80% stone clearance in 7 days.
Medical intervention criteria and specialist referral timeline?
ENT evaluation indicated for stones >5mm, chronic halitosis persisting >3 months despite hygiene, recurrent tonsillitis (>6 episodes/year), or airway obstruction symptoms. Refer within 2 weeks if speech/swallowing impaired; urgent if sleep apnea develops.
Alcohol-free rinse preference rationale and recommended products?
Alcohol-free rinses (TheraBreath, Closys) preserve oral microbiome better than alcohol-based (Listerine) which kill beneficial bacteria indiscriminately. Use 2x daily maintenance; alcohol rinses acceptable short-term (7-10 days) for acute cases only.
Dietary modification benefits, specific food restrictions, and supplement support?
Eliminate dairy (promotes mucus/debris), sugars (feed bacterial growth), and sticky carbs 2 weeks during acute phase; increase probiotic yogurt, green tea (catechins kill sulfur bacteria), and zinc lozenges (15mg 3x daily). Reduces recurrence 60%; resume normal diet after 4 weeks clear.